Reading Turnitin similarity reports – look beyond the score
Written by Jim Lusted, Learning Designer/Senior Lecturer in Sport Studies
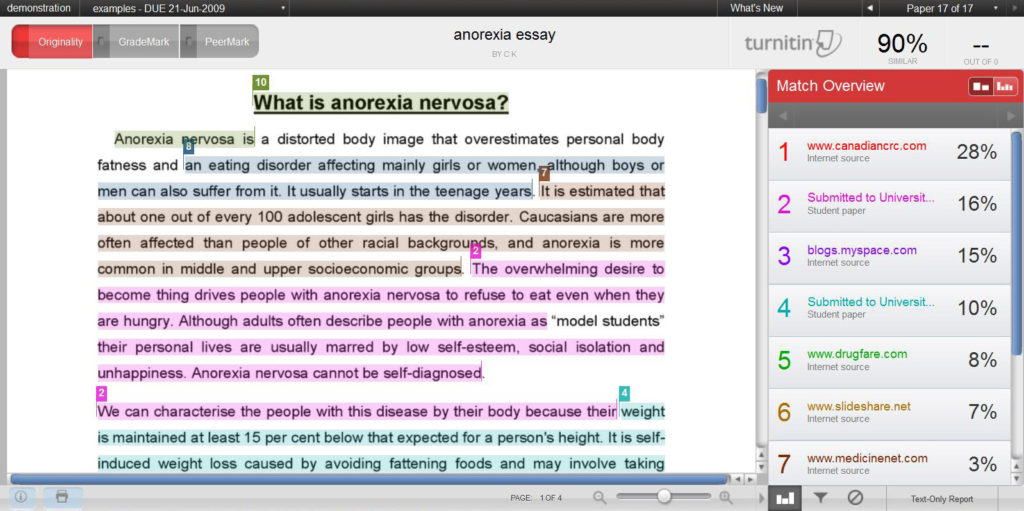
Since the University moved to online assignment submission some years ago it has been much easier to judge the originality of student work. If an assignment is set up using a Turnitin submission point, a similarity report is automatically generated for each assignment. This provides the marker with a % score of how much of the student work matches material contained in Turnitin’s vast database – some 62 billion webpages, 734 million student papers and 165 million academic sources.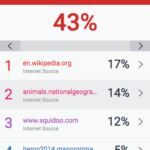
While this automated process has really helped staff judge the credibility of student assignments, your own judgement is still needed to interpret the similarity report. This blog offers some tips about how to ‘read’ Turnitin reports – and to consider a range of factors beyond just the overall similarity % score to help you make a judgement about whether you should refer an assignment to the academic integrity and misconduct process.
Get the set up right to get the most accurate report
Start by making sure the similarity report generated is as accurate and useful as possible. When you first set up a Turnitin submission point in NILE, you are offered a daunting list of options to select from. Follow this help guide from the LearnTech team to ensure your similarity reports check exactly what you want them to.
Before you begin marking, a useful tip is to overlay the similarity view with the marking view of the Turnitin site (see right).  This allows you to continually keep a check on originality as you go through the process of marking the work – and helps you contextualise the areas of similarity. You’ll be able to easily spot where exactly the larger pockets of similarity are being used across the assignment.
This allows you to continually keep a check on originality as you go through the process of marking the work – and helps you contextualise the areas of similarity. You’ll be able to easily spot where exactly the larger pockets of similarity are being used across the assignment.
Look beyond the percentage score..
The overall % score gives us a quick, rough indicator of how original a student submission might be. It’s certainly a good starting point, but it shouldn’t solely determine your verdict of the assignment and it’s really best not to set a benchmark score to guide your overall judgement – the process ultimately requires a qualitative judgement to be made. Let’s look at a couple of scenarios where the percentage originality score (high or low) might not necessarily tell the full story of who has written the assignment.
a) A small score but a big problem?
Anything below 20% is fine, right? A score like this does indicate that the vast majority of the assignment is original. But…
- A small percentage score could ‘hide’ one or two (or more) long paragraphs of ‘copied’ text that is acknowledged as such. While only taking up a small proportion of the assignment, such large chunks of unsourced text may lead you to concerns about possible plagiarism.
- A similarity score of zero may also raise some concerns. If an assignment contains absolutely no material derived from other sources, particularly if you are sure that the work contains the use of quotes and paraphrasing, you may want to question why the report is so ‘squeaky-clean’. There are all kinds of tips on the internet for students to try to ‘trick’ Turnitin that might possibly be at play. You might also be entering the world of contract cheating, which is much harder to identify (and prove).
b) A big score but with good reason?
Anything over 30% must be a problem, right? Not necessarily – ask whether there might be any plausible reasons for the large score, particularly if it is repeated across several students in your cohort. Potentially valid reasons for high similarity scores might include:
- The use of a generic template or pro-forma that students have used to structure their assignment – is this the primary cause of the high score?
- The inclusion of appendices in a student’s work are these being highlighted?
- Several students referring directly to the same source or quote or content (e.g. a prescription protocol) that has been used regularly in the module
- Several small passages of quotes being used appropriately and suitably referenced
Look beyond the similarity score – there may be a perfectly good reason for the relatively high % score.
The grey areas where your judgement is needed
This may all sound straightforward, but there are always going to be difficult judgements to be made when cases are not as clear cut as those above. The ‘grey areas’ tend to relate to two main areas:
1. Paraphrasing another source – is the student trying to re-phrase another person’s work? Some students are better at this than others, and there are online tools like Grammarly that students may be tempted to use to help paraphrase (often with poor results). You need to decide whether this paraphrasing is a deliberate attempt by the student to claim the work as their own, or more a case of poor academic practice.
2. Referencing – are the sections under scrutiny indicative of a student presenting the work of others as their original efforts, or perhaps the result of poor referencing practice? Consider the quality and style of referencing through the work (good or bad) to help decide how ‘deliberate’ the student is being in failing to acknowledge other sources of work. Again, the judgement here is between willful academic misconduct or poor academic practice.
In these types of ‘grey’ cases, its best to seek a second opinion – from a trusted colleague, an experienced member of your team or even a quick chat with an Academic Integrity Officer (AIO) before you decide whether to formally refer the student to the academic integrity and misconduct process. Getting a second opinion usually helps you come to the right verdict in the end.
Recent Posts
- H5P (HTML5 package) content types meets the needs of Jim Atkinson, Staff Development Trainer
- Blackboard Upgrade – July 2025
- StudySmart 2 – Student Posters
- NILE Ultra Course Award Winners 2025
- Blackboard Upgrade – June 2025
- Learning Technology / NILE Community Group
- Blackboard Upgrade – May 2025
- Blackboard Upgrade – April 2025
- NILE Ultra Course Awards 2025 – Nominations are open!
- Blackboard Upgrade – March 2025
Tags
ABL Practitioner Stories Academic Skills Accessibility Active Blended Learning (ABL) ADE AI Artificial Intelligence Assessment Design Assessment Tools Blackboard Blackboard Learn Blackboard Upgrade Blended Learning Blogs CAIeRO Collaborate Collaboration Distance Learning Feedback FHES Flipped Learning iNorthampton iPad Kaltura Learner Experience MALT Mobile Newsletter NILE NILE Ultra Outside the box Panopto Presentations Quality Reflection SHED Submitting and Grading Electronically (SaGE) Turnitin Ultra Ultra Upgrade Update Updates Video Waterside XerteArchives
Site Admin